The 1s orbital energies of Li C and F all lie well below that of the H 1s orbitalThe charge densities of these inner shell orbitals are tightly bound to their respective nuclei. Draw the MO diagram for B_2.

9 7 Molecular Orbital Diagrams Youtube
Boron has 2 electrons in the 2s orbitals and 1 electron in the 2p orbital.
. Fill molecular orbitals using energy and bonding properties of the overlapping atomic orbitals. AO2px AO2px π2px π 2px weak sidelong overlap AO2py AO2py π2py π 2py weak sidelong overlap AO2pz AO2pz σ2pz σ 2pz strong head-on overlap Thus we take 10 atomic orbitals and generate 10 molecular orbitals in. ψ ψ ψ ψ ψ.
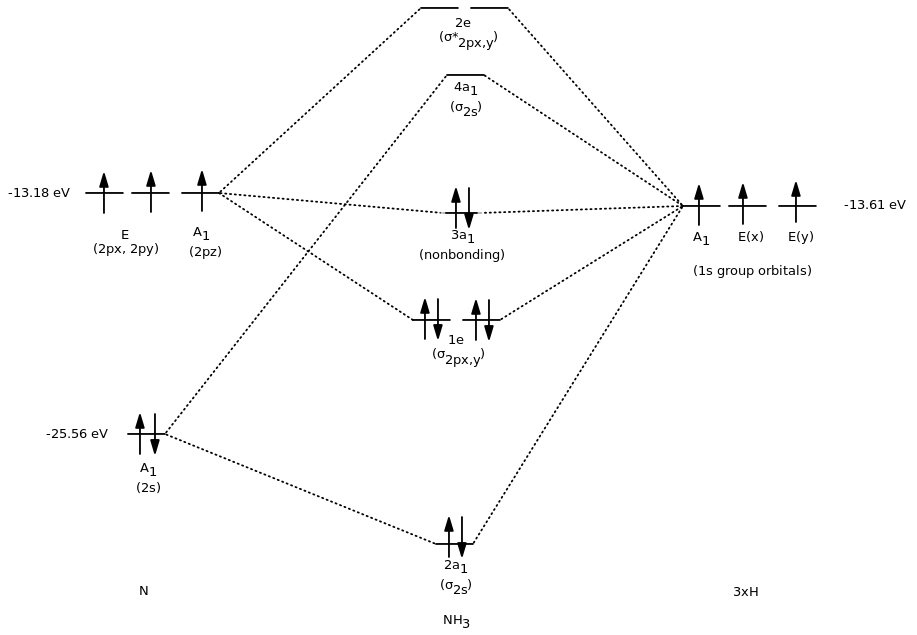
3H A_1 with N A_1 bonding antibonding 3H Ex with N E bonding antibonding 3H Ey with N E bonding antibonding Nothing with N A_1 nonbonding Using the orbital potential energies Appendix B9 of each atom we eventually get. The F 2s is nonbonding. HF nb σ σ Energy H 136 eV 1s F 186 eV 402 eV 2s 2p So HF has one σ bond and three lone electron pairs on fluorine.
Draw the atomic and hybrid orbitals on on side of the page. Use the diagram to predict properties of the molecule. Note that we came in with seven orbitals 3xxH N_2s N_2p_x N_2p_y.
Thats it for the MO diagram of B_2. Our primary goal for today is to be able to draw diagrams of molecules such as we see in figure 1. Due to symmetry of the molecule homonuclear MOs are less difficult to derive than heteronuclear molecules and polyatomic molecules.
Overlapping atomic orbitals produce molecular orbitals located in the middle of the diagram. In polyatomic molecules we can have more than two atoms combining eg. Together to produce a sigma molecular orbital σ 1sa 1sb.
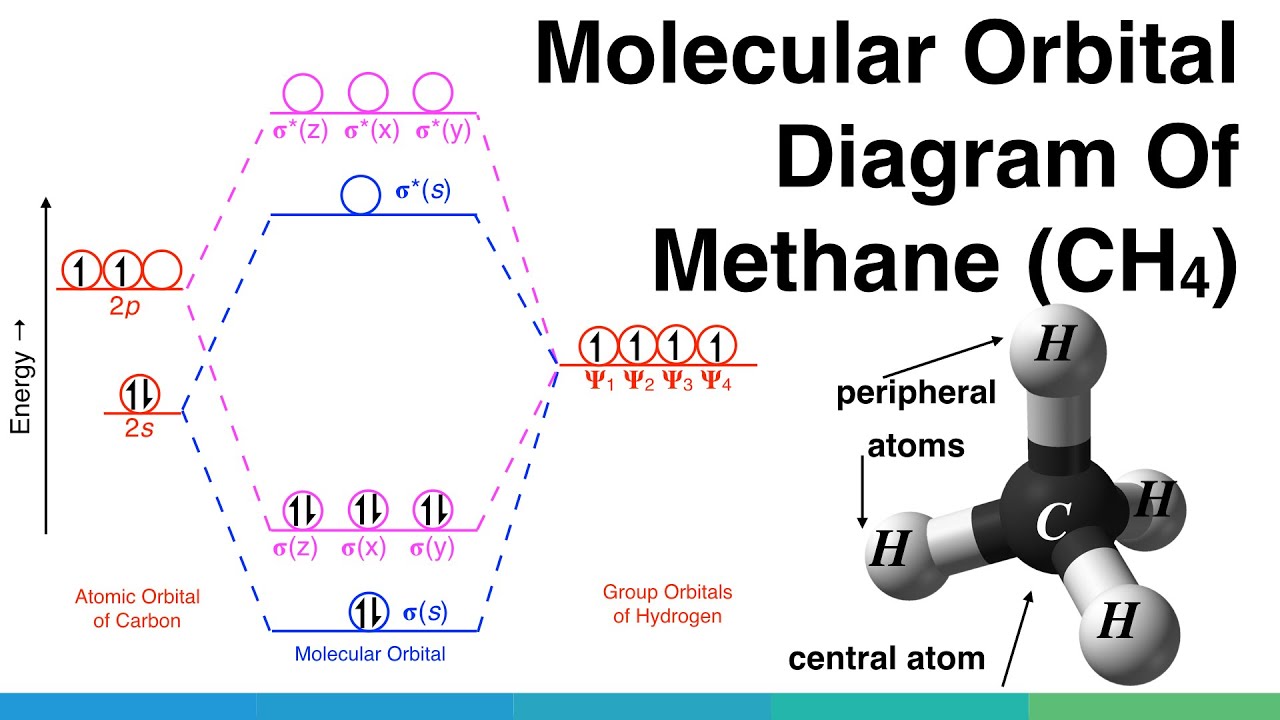
Protocol for constructing MO diagrams for AH n H 2O NH 3 CH 4 1 Identify symmetry equivalent atoms hydrogens in this case 2 Generate Symmetry Adapted Linear Combinations on these identical atoms 3 Combine SALCS with orbitals on A For more complex molecules there may be more than 2 symmetry equivalent types of atoms. Symmetry properties and degeneracy of orbitals and bonds can be. Procedure for Constructing Molecular Orbital Diagrams Based on Hybrid Orbitals 1.
Decide how many orbitals each atom needs to make its sigma bonds and to hold its non-bonding electrons. The orbitals will combine like so. C Calculate the average CC bond order based on.
In this case were using the standard one. They should not therefore be much affected by the field of the proton or interact significantly with the H 1s orbital. First step is to determine which MO diagram were using.
Molecular Orbital Theory MOT for Polyatomic Molecules MO diagram for polyatomic molecules by Ved Sir only on Chem Academy YouTube ChannelFree Study Mater. Polyatomic Molecular Orbital Theory Transformational properties of atomic orbitals Atomic orbital Transforms as s x2y 2z 2 px x py y pz z dz2 z2 2z 2-x2-y2 dx2-y2 x2-y2 dxy xy dxz xz dyz yz S py When bonds are formed atomic orbitals combine according to their symmetry. 8 - Drawing Molecular Orbital Diagrams.
Sp3d hybrid orbitals one s three p and onedatomic orbitals mix to form a set of five orbitals with different directional properties. 01-01-2022 The molecular orbital diagram of ethane would be. A second molecular orbital is also created which we simplistically show as a subtraction of the two atomic 1s orbitals σ 1sa - 1sb.
Draw out the MO diagram and label in the valence electrons. Indeed molecular orbital theory forms the basis for most of the quantitative theoretical investigations of the properties of large molecules. Depending on if it is a homonuclear case where the bonding atoms are the same or a heteronuclear case where the bonding atoms are.
ψ ψ ψ ψ ψ. These diagrams tell us that the F 2 molecule has a single bond the CO 2 molecule has two double bonds and the HCN molecule has one single bond plus one triple bond. Sp3_hybrid2 s xpz 1.
In this video qualitative MO diagrams will be generated for simple polyatomic molecules water ammonia and difluorocarbene using so-called ligand group o. The Y-axis of a MO diagram represents the total energy not potential nor Gibbs Energy of the orbitals. MAKE SURE TO SUBSCRIBEThis video puts emphasis on molecular orbital diagrams a fundamental way of understanding why Diels-Alder chemistry works.
FUNDAMENTAL STEPS IN DERIVING MO DIAGRAMS. Since the electrons in this orbital are more stable than on the individual atoms this is referred to as a bonding molecular orbital. I show the relative energies of the molecular orbitals ii draw a picture of each molecular orbital iii label each molecular orbital as bonding nonbonding or antibonding iv include electrons on your diagram.
General Notes on Molecular Orbital Diagrams 1. There are two main methods for constructing such diagrams. Such as H 2 O NH 3 and CH 4.
The concept of a molecular orbital is readily extended to provide a description of the electronic structure of a polyatomic molecule. Begin with the Lewis structure. This orbital is called sigma-star σ and is less stable.
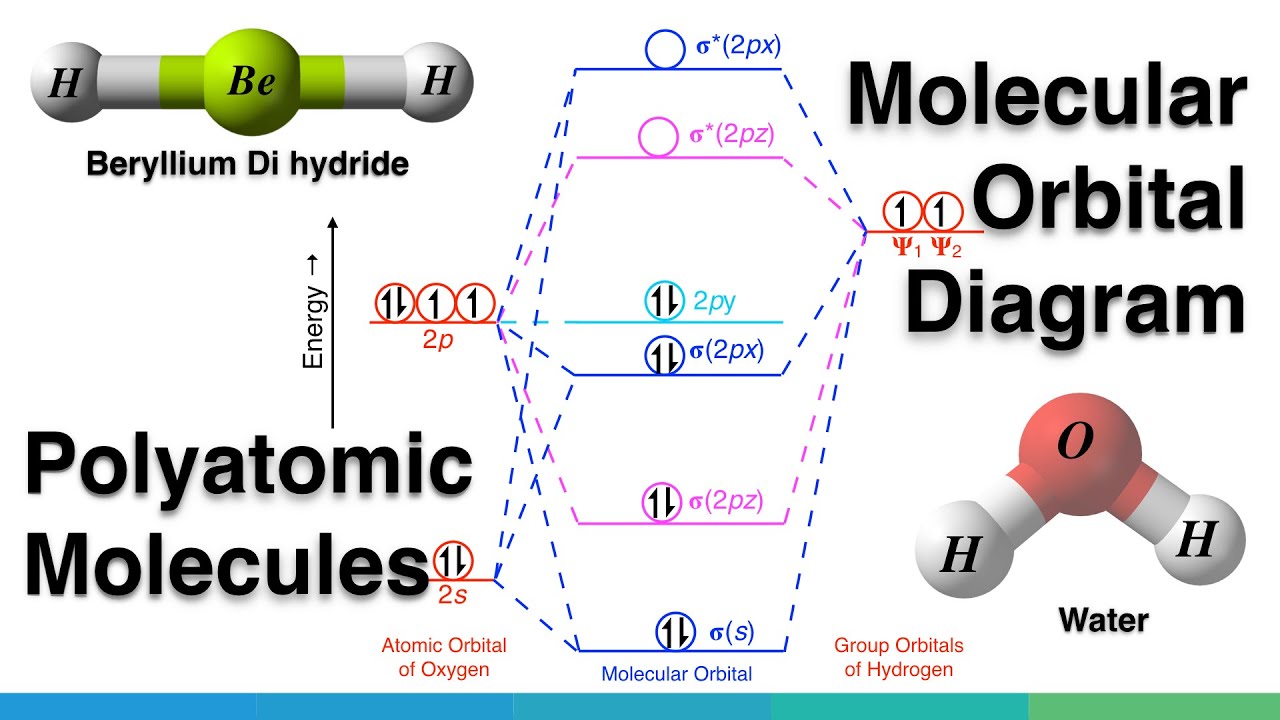
The molecular orbital of lowest energy in these molecules the ls molecular orbital should be. Carbon dioxide CO2 molecule is triatomic and linear like Beryllium di hydride BeH2 However unlike hydrogen as peripheral atoms in BeH2 there are oxyge. Molecular Orbitals for Polyatomic Molecules.
The molecular orbital is formed from the combination of atomic orbitals which must have nearly the same energy and are symmetrical about the molecular axis. Sp3_hybrid2 2s 2px 2py2pz 1. In case of beryllium hydride there are 3 atoms overlapping simultaneously.
MO Diagram for HF The AO energies suggest that the 1s orbital of hydrogen interacts mostly with a 2p orbital of fluorine. ψ ψ ψ ψ ψ. Abstract TLDR Molecular orbital diagrams are a fantastic way of visualizing how molecular orbitals form using what we already understand about sigma and pi bonds.
Individual atomic orbitals AO are arranged on the far left and far right of the diagram. Find the valence electron configuration of each atom in the molecule. For each sigma bond take a hybrid or atomic orbital from each atom.
To understand the MO diagram of ethane we consider it as a homonuclear diatomic A2 molecule. Decide if the molecule is homonuclear of heteronuclear. Building Molecular Orbital Diagrams for Homonuclear and Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecules.

Molecular Orbital Mo Diagram Of Polyatomic Molecules Beryllium Dihydride Beh2 And Water H2o Youtube

Molecular Orbital Diagram Of Polyatomic Co2 Molecules Chemical Bonding Molecular Structures Youtube
Molecular Orbital Mo Diagram Of Polyatomic Molecules Beryllium Dihydride Beh2 And Water H2o Youtube

Molecular Orbital Mo Diagram Of Polyatomic Molecules Beryllium Dihydride Beh2 And Water H2o Youtube
0 comments
Post a Comment